User's Manual for i18n4data
By Huang Neng Geng
1 Overview
The i18n for data (abbreviated as i18n4data) provides a solution to manage the complexity of creating internationalized web applications developed using Java. The i18n4data has similar functionality to the internationalization available in the i18n tag library under Apache Software Foundation, but was implemented in a different way.
The name of i18n for data means that the internationalization is not only for interface message, but also for user's data. By using i18n4data, an application developer is able to make an existing java web project internationalized with least coding. It also helps to develop a new internationalized java web project by reducing the work on data structure design and software design related to language problems.
The i18n4data is a java servlet filter to make your java based project internationalization. It supports the translation of both interface message and user's data to various languages. There are two build in dictionaries to fulfill the task. The two dictionaries are for messages and user's data separately, which are maintained by you through a build in servlet page. Therefore, the user's data will be translated into various languages exactly defined by you. This is truly important for those who want to publish their information with precise meaning into different languages.
2 Installation
2.1 System requirements
The i18n4data requires no software other than a servlet container that supports servlet filter feature. The following environments has been tested and should work properly:
- apache tomcat 5.5.23
- If anyone who successfully installed in other environment, please let me know.
2.2 Installation
1. Download i18n4data from sourceforge.net.
2. Uncompress it to your web application directory, for example,
- C:\tomcat-55\webapps\yourwebproject under Windows
- /usr/local/ tomcat-55\webapps\yourwebproject under Linux/Unix
Note: If asked to overwrite existing hsqldb.jar file, you may choice to overwrite it with the one shipped from i18n4data.gz.tar, which is 1.8.0.9 version. If you meet any problems later, you may need to replace it with the old one.
3. Copy following content and paste it into file web.xml in directory WEB-INF. Then restart your application server.
- <filter>
- <filter-name>I18n4dataFilter</filter-name>
- <filter-class>org.ngpage.i18n4data.filter.I18n4dataFilter</filter-class>
- </filter>
- <filter-mapping>
- <filter-name>I18n4dataFilter</filter-name>
- <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
- </filter-mapping>
- <servlet>
- <servlet-name>I18nEditData</servlet-name>
- <servlet-class>org.ngpage.i18n4data.I18nEditData</servlet-class>
- </servlet>
- <servlet-mapping>
- <servlet-name>I18nEditData</servlet-name>
- <url-pattern>/i18n/I18nEditData</url-pattern>
- </servlet-mapping>
- <servlet>
- <servlet-name>I18nEditMessage</servlet-name>
- <servlet-class>
- org.ngpage.i18n4data.I18nEditMessage
- </servlet-class>
- </servlet>
- <servlet-mapping>
- <servlet-name>I18nEditMessage</servlet-name>
- <url-pattern>/i18n/I18nEditMessage</url-pattern>
- </servlet-mapping>
Note: It should be inserted under the root node of the xml file. That is the line after <web-app> node.
4. (Optional) Make changes to configuration file WEB-INF /i18n4data.xml or your source code (if it is AJAX enabled) to meet your need.
5. That's all. Run your application and enjoy it.
3 Definition of terms
Unlike i18n message bundle, all the translations in i18n4data are stored in a database. Bellow are some definitions used in i18n4data:
- key: A key is a word or phrase to be translated, which may be textual user's data or textual message. In i18n4data, a key also contains its catalog prefix, separated by a dot. In this way, a key should be in the form of "catalog.keyName". For example, a key for product name "Printer" should be "product.Printer". The language of a key is arbitrary. Therefore, a Chinese product name also may be assigned as a key. It's up to the end user's choice. The character "@" has special meaning in i18n4data. If a key is start with @ then the message will not be encode.
- catalog: Each key has a prefix to indicate its belongs. For example, all keys of product name have same prefix "product". The language of a catalog is arbitrary, too. A catalog name should not have dot symbol (".") because the dot is used as a delimiter between catalog and key.
- key name: Key name is the last part of a key. In i18n4data definition, a key consists of catalog and key name, separated by a dot ".". In the example of key "product.Printer", "product" is catalog, "Printer" is key name, and "product.Printer" is a key.
- translation: A key has translation for each language. For example, key "product.Printer" has translation of "Printer" in English, "Imprimante" in French, "Drucker" in Germany and "妞忘扶扯快抖攸把扼抗我快 找抉志忘把抑" in Russian.
- key entry: A key entry is the combination of key (key name and catalog), catalog, and translations. For example, the key entry for product "product.Printer" is {"product.Printer", "product", "Printer", "Imprimante", "Drucker","妞忘扶扯快抖攸把扼抗我快 找抉志忘把抑"}.
- dictionary: A database to store all key entries. The i18n4data translates all keys by searching in the dictionary. Textual user's data and textual interface message are stored in different tables of same database by default. This can be configured in configuration file (i18n4data.xml).
- interface message: This is textual message that is coded in application, such as page title, operation instruction. The i18n4data call it message briefly.
- user's data: These are textual user's data that are input by users and saved in database, such as product name, category name. The i18n4data call it data briefly.
4 A quick look
The treatment of interface message is automatically done by i18n4data. However, for the user's data, there are some differences.
1. Textual user data (such as product name) that are recognized as keys are treated in the following way:
- When a user type input from keyboard:
- a user input a key name from client browser;
- i18n4data convert it into a key by adding catalog prefix and save to the database;
- When a user access to browse data:
- web application retrieve a key from database;
- i18n4data convert it into translation and response to client browser.
Therefore, an end user will read translations of one language the user select rather than the original key name.
When a key is located in a form (input text field or hidden field), it will be remained in the original form, that is to say, not to be translated. For AJAX enabled pages, it is a little different way and will be discussed later.
2. Non-textual user data (numbers, date, long text such as description) will not be recognized as a key and will be treated in a normal way.
5 Guide for end users
The web application has the same user interface after internationalized by i18n4data. End users of the web application use it in the same way only in one exception.
If i18n4data filter mode is set to auto, it is the responsible of end users to define a key. To define a key, the end user should input the text data with a preceding character "\". Then i18n4data will treat that text as a key. If a user want to input a text with leading "\", the user may input the text with double "\\", which indicates that there one "\" as text.
If i18n4data filter mode is set to code, it is the responsible of application developers or application administrators to define key fields. After define key fields, end users use the application exactly the same as before.
In both mode (auto and code), it is necessary for staff to maintain the dictionary. When a new key is added, the dictionary (database) will insert that key a new record. And staff should translate it into different languages. These can be done through an edit page provided by i18n4data. The link for edit page is automatically added at the bottom of each page by default. For a big system like an ERP system, the translation work might be very huge.
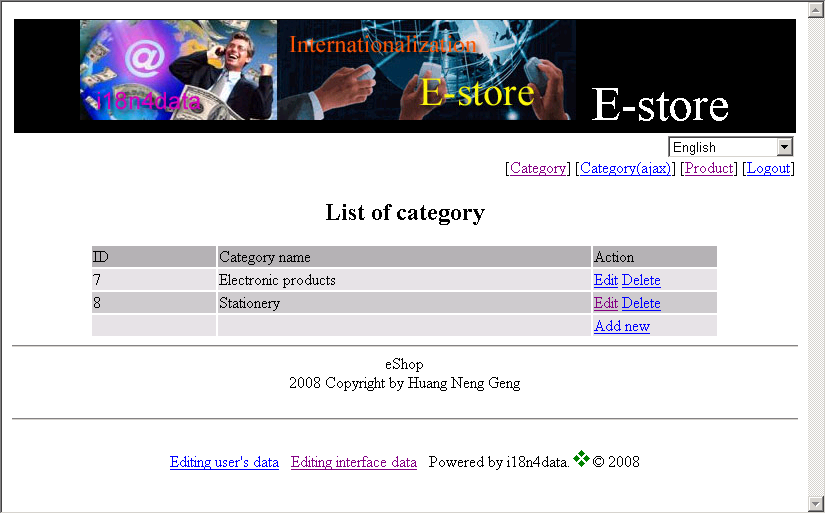
Fig. 1 e-shop interface in English
Fig. 1 showed an example of e-shop web site. When users select a language from the drop down menu and refresh the page, all message and data will change to the selected language.
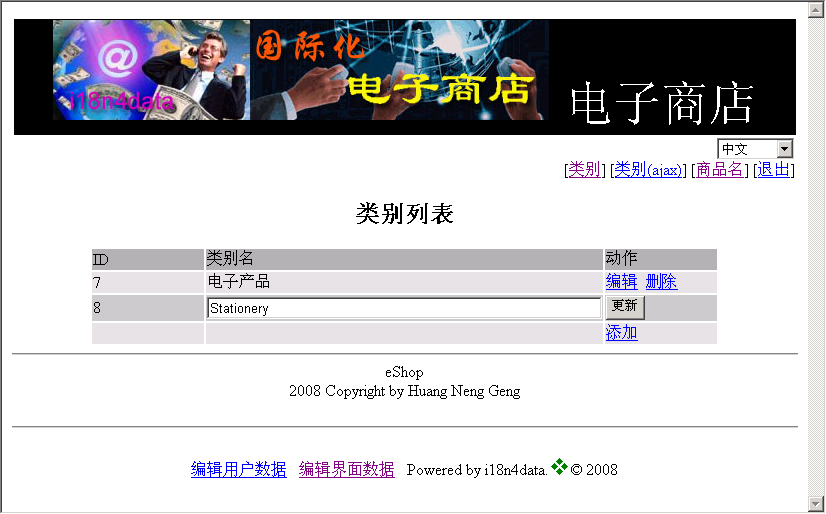
Fig. 2 e-shop interface in Chinese (editing a key)
Fig. 2 showed a key is being edited. The key name is in English and displayed in a text box field in a form for editing. The key will be translated into text of selected language after editing if the dictionary has the translation for that language (Fig. 3).
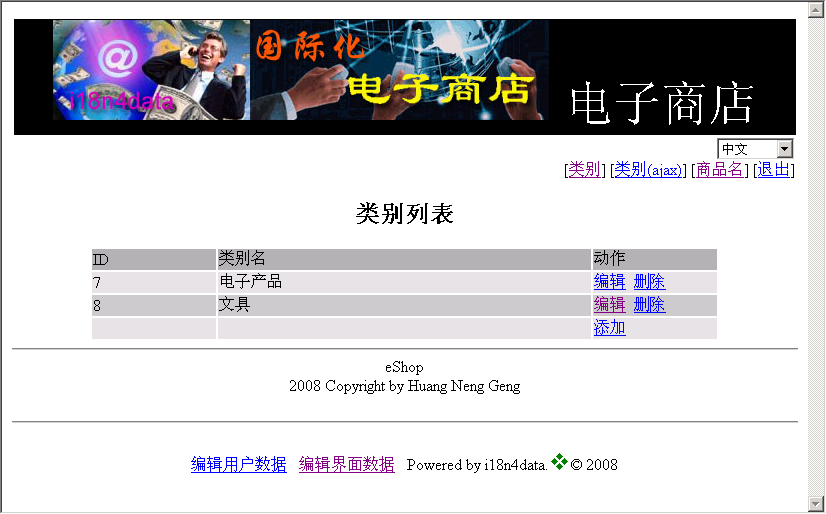
Fig. 3 e-shop interface in Chinese (after editing)

Fig. 4 A new key is displayed
Fig. 4 showed a new key is create and displayed as "[catalog.key name]" because it does not have any translations in the dictionary. It will remain the same until translation for that key is added.
6 Guide for maintenance
The maintenance work of dictionaries for i18n4data is huge. Fortunately, i18n4data provides an easy interface for dictionary maintenance.
All key entries are inserted into the dictionary automatically by i18n4data. If i18n4data fails to find a key entry, it will insert a record in the dictionary.
A key entry could be deleted from the dictionary manually. The deletion is permanent. If a key entry is deleted and i18n4data fails to find the key entry later, i18n4data will create the key entry again. However, the new key entry does not have correspondence translations and need to be translated again.
Key name and catalog could not be modified after it was created. Only translations are editable.
All key entries are organized by catalog. Maintenance users may browse entries by catalog or by searching criteria or both. Translations for three languages are displayed. Users may edit translations for all languages of a key entry at the same time. Users also may edit all selected key entries of translation for only one language at the same time. Users also may select all key entries that do not have translation of one language.

Fig. 5 Browsing the dictionary
There are two dictionaries, one for interface message, one for user's data. Fig. 5 showed interface message key entry list. An user may select a working language from menus at the up right corner. An user may click to![]() reload the dictionary (also reload i18n4data configuration file). Select
reload the dictionary (also reload i18n4data configuration file). Select
![]() to list all key entries that do not have translation for one language. Click key entry to edit the key for all languages (Fig. 6). Select
to list all key entries that do not have translation for one language. Click key entry to edit the key for all languages (Fig. 6). Select
![]() to edit all key entry for one language (Fig. 7).
to edit all key entry for one language (Fig. 7).

Fig. 6 Editing a key

Fig. 7 Editing keys for one language
For security reason, not all users are able to edit the dictionary. The permissions are assigned by administrators.
7 Guide for application administrators and developers
The i18n4data is developed by using Java 5.0. The development environment is:
- Eclipse 3.2 + MyEclipse 6.0.
- Apache tomcat 5.5.23
- HSQL 1.8
For application administrators and developers, only limited JSP knowledge is required to configure i18n4data to work properly with the application.
To understand the work that i18n4data doing, it is explained how the i18n4data works, which is the basic of i18n4data. However, this knowledge is not a must to understand i18n4data.
7.1 Mapping and filter
The i18n4data uses servlet filter technology to filter all request and response to fulfill the key identifying and translating work.
1 Field-mapping
Each key name will have a catalog prefix, which is maintained by i18n4data automatically. The i18n4data achieves it by maintaining a field-mapping table, in which a table contains form's field and catalog pairs are stored. When user's data is sending to web server by POST method, the form's field name will be sent to server at the same time. Then i18n4data check the form's field name of the user data and find out the correspondent catalog for it. The user's data which are not associate with a catalog is not recognized as a key.
Note: The form's field name is defined in HTML file, typically a text box input field. It is not the column's name of a table in database.
2 Filter request
It happens when a web server receives users data input (request). After receiving the request, at the server end, the i18n4data will treat every input data in following way:
1. First, look for page based field mapping. If found, use the catalog prefix.
2. If not found, look for global (configuration based) field mapping. If found, use the catalog prefix.
3. If still not found, then
If in auto mode or development mode, check user*s input:
- If the user's data start with "\", it is recognized as a key. Then i18n4data will try to find the attached catalog with the key. The attached catalog is first part of text in user's data, separated by a dot ".". For example, user's data like "\product.printer" means a key with attached catalog "product" and key name "printer". If no attached catalog found, then use form's field name as catalog. For example, user's data like "\printer" means a key without attached catalog but key name "printer". In this case, the i18n4data will use form's fields name as catalog.
- If the user's data start with "\\", it is NOT recognized as a key. Delete one \, then treat it as normal data.
- If in development mode, i18n4data will record the field-catalog relationship (mapping) into an xml file for easy configuration. The mapping is added to the global mapping in memory, too.
4. Otherwise, user's data is NOT recognized as a key even start with "\". Then treat it as normal data.
3 Filter response
It happens when a web server sends data to users. Before sending the response, at the web server end, the i18n4data will filter the text and make translation to keys.
1. For normal html contents: The i18n4data filter user*s data and interface messages and response translate for these keys. For example, a key "\product.printer" will be translated into "Imprimante" in French.
2. For AJAX contents: The i18n4data filter all interface messages and response translate for them. For user*s data, i18n4data response the key enclosed by HTML remark tags in addition to the translation. For example, a key "\product.printer" will be translated into HTML code "<!--i18n4data-key= product.printer--> Imprimante" in French. In this case, "<!--i18n4data-key= product.printer-->" is used by JavaScript in the client browser.
7.2 Database
The i18n4data uses hsqldb-1.8.09 to store the dictionaries by default. There are no views, stored procedures, and triggers. It should work on most database management system. A best practice is to store interface message dictionary in hsqldb and store the user data's message dictionary in the database used by application. This strategy may help to maintain the consistence between application data and user data's message.
7.3 Configuration
Application administrators and developers are responsible to make settings in configuration file (i18n4data.xml). Bellow is an example:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <!-- i18n4data configuration file, 2008-1-26 Copyright by Huang Neng Geng -->
- <!-- for more information, see i18n4data user manual
- or visit http://www.ngpage.org/i18n4data -->
- <i18n4data-configuration>
- <supported-language-list>en,fr,de,ru,zh_CN</supported-language-list>
- <security-level>none</security-level>
- <default-language-mode>on</default-language-mode>
- <debug-mode>off</debug-mode>
- <development-mode>on</development-mode>
- ﹛
- <filter>
- <path-pattern>
- <path>.*</path>
- <filter-mode>code</filter-mode>
- <field-mapping>
- <field></field>
- <catalog></catalog>
- </field-mapping>
- </path-pattern>
- <path-pattern>
- <path>/servlet/CategoryList.*</path>
- <filter-mode>auto</filter-mode>
- <field-mapping>
- <field>name</field>
- <catalog>CategoryName</catalog>
- </field-mapping>
- </path-pattern>
- <path-pattern>
- <path>/servlet/ItemList.*</path>
- <filter-mode>auto</filter-mode>
- <field-mapping>
- <field>name</field>
- <catalog>Product</catalog>
- </field-mapping>
- </path-pattern>
- </filter>
- ﹛
- <jdbc-data>
- <driver></driver>
- <url></url>
- <user></user>
- <password></password>
- <table-name></table-name>
- </jdbc-data>
- ﹛
- <jdbc-message>
- <driver></driver>
- <url></url>
- <user></user>
- <password></password>
- <table-name></table-name>
- </jdbc-message>
- ﹛
- <navigation>
- <navigation-mode>auto</navigation-mode>
- <edit-page-url-data></edit-page-url-data>
- <edit-page-url-message></edit-page-url-message>
- </navigation>
- ﹛
- <ajax-content>
- <ajax-key-open-tag></ajax-key-open-tag>
- <ajax-key-close-tag></ajax-key-close-tag>
- <ajax-translation-open-tag></ajax-translation-open-tag>
- <ajax-translation-close-tag></ajax-translation-close-tag>
- </ajax-content>
- </i18n4data-configuration>
﹛
Note on configuration file:
1. Supported languages: The i18n4data uses the standard country code and language code for languages. The number of languages supported by i18n4data does not have limit.
2. Security level:
- (default) none: Without any security at all. In this security level, every user may edit all keys.
- full: With full security. In this security level, every user should have permissions to edit keys. The permissions are defined through catalog list set by administrator.
3. Default language mode: If set on, when a translation for one language could not found, use default language's translation. Note: Default language is deferent from system language.
4. Debug mode: For developers use only.
5. Development mode
- (default) off:
- on: This is only for developers. Developers may define a catalog by using ※/catalog.key name§. All mapping are saved in an xml file in this mode. The file is i18n4data-date-time.xml under directory "/WEB-INF/". The date-time in the file name are automatically replaced by current date and time. Developers may then add this information to configuration file (i18n4data..xml).
6. Filter
a) Path: Each mapping will to match a path to take effect. The path may be an exactly a real path, start from the project root path, such as "/admin/itemList.jsp" or "/servlet/ItemList". The path may also contains wildcard character, such as "/servlet/Item.*" means to match "/servlet/ItemList", "/servlet/ItemXX", and "/servlet/Item.do", etc. Note the wildcard character IS ".*' rather than "*".
b) Filter mode:
- (default) auto: In this mode, i18n4data will automatically detect the user's input. All input text start with "\" are treated as keys and be saved in the dictionary. For example, if a user input text "\Calculator" in a input field, i18n4data will treat it as a key. Then i18n4data strip the back slash character "\", add a catalog, and save the key "catalog.Calculator". After the user edit its translation for languages, this key will be displayed in different languages in the screen. In this mode, developers of the application are not required to modify source code at all. End users are responsible to define which input text is a key.
- code: In this mode, only those input fields set in configuration file or application source code are treated as key fields. As the result, all input text in those input fields are treated as keys. There is no requirement for end users to type "\" to define a key. The administrators or developers of application is responsible for define a key mapping list (field-catalog mapping) in configuration file or application source code. The catalog is automatically inserted in the beginning of input text. For example, if a user input text "Calculator" in product name text input field, i18n4data will treat it as a key and automatically add catalog "product" and a dot before it. So the key becomes "product.Calculator". If a user input the same text "Calculator" in a text input field without mapping defined be developers, the text will not be treated as a key.
- none: means no filter in any situation.
c) Filter mapping: To define a field-catalog pair.
7. jdbc-data: The parameters in this section is to define jdbc parameters for user's data dictionary.
8. jdbc-message: The parameters in this section is to define jdbc parameters for interface message dictionary.
9. Navigation mode:
- (default) auto: Automatically add navigation links to edit pages at bottom of every pages.
- code: It is the responsibility of developers to add navigation links in pages. In this way, the navigation links may be put into only some pages or in a place rather than the bottom of pages.
10. ajax-content: This is for AJAX enabled page. If defined in following way:
- <ajax-key-open-tag>[tag1]</ajax-key-open-tag>
- <ajax-key-close-tag>[tag2]</ajax-key-close-tag>
- <ajax-translation-open-tag>[tag3]</ajax-translation-open-tag>
- <ajax-translation-close-tag>[tag4]</ajax-translation-close-tag>
A key "\product.printer" will be translated into HTML code "[tag1]product.printer[tag2][tag3]Imprimante[tag4]" in French.
7.4 Code modification
1 Dealing with interface message
The developers of application should make changes to codes to deal with interface message's translation. There are three methods in I18nMessage for developers to define an interface message key:
- public static String getMessage(String catalog, String message)
- public static String getMessage(HttpServletRequest request, String message)
- public static String getMessage(HttpServletRequest request, String message, boolean isPageBased)
In the jsp page, find every message that should be translated, and use one of above method to convert it into a key.
An example would be look like this:
- <%@ page import="org.ngpage.i18n4data.*" %>
- <%=I18nMessage.getMessage("eshop_customer", "List of goods") %>
In this case, a key called "eshop_customer.List" is defined and automatically insert into the message dictionary. Before it is translated in the dictionary, it will be displayed as "[eshop_customer.List]", which means it is a key in the entry of the dictionary. After it is translated, it will be displayed as a translation.
For details about these methods, see API document included in the package.
2 Dealing with user's data
The difference between the translation of interface message and user's data is the way a key is defined. Instead of change the application codes to define a key, a configuration file is used to define which form's field should be a key.
3 Global configuration
Sometimes, it is necessary to make changes to i18n4data configuration to use its advanced feature. These changes include:
1. Set current language.
2. Set security for different users.
3. Set page based field-catalog mappings.
4. and more
The i18n4data provides a set of API for application developers. See 7.6 API document.
7.5 Make a search
It is always a good idea to provide end users search function. The i18n4data provides an API that return keys from search string of translation in a given language.
For details, see code in examples.
7.6 AJAX problem
The i18n4data support AJXA enabled pages. In this case, the i18n4data have to communicate to client JavaScript code in a different way. The i18n4data provides an API and features to fulfill this task.
For details, see code in examples.
7.7 API document
The i19n4data provides some API for application developers. Bellowing are a brief description to the API. For more information about them, see standard java doc API documents.
- l String findKeys(String search, String catalog, String language): This is a method to search string in a translation and return the key(s).
- l String getLanguageMenu(HttpSession session) To get a string that contains all languages list in an HTML drop down menu format.
- l String getMessage(HttpServletRequest request, String message, boolean isPageBased) To define an interface message that will be translated into language an end user select.
- l String getMessage(String catalog, String message) To define an interface message that will be translated into language an end user select.
- l void removeI18n4AllSettins(HttpSession session) This method is to remove all above session settings.
- l void setAjaxTags(HttpServletRequest request, String[] ajaxTags)
- l void setAjaxType(HttpServletRequest request) Indicate current page as a AJAX page, which means i18n4data will not only return translation, but also the original key back to client browser.
- l void setAjaxType(HttpServletRequest request, String ajaxType) Similar to setAjaxType(HttpServletRequest request), but has one parameter more.
- l void setLanguage(HttpSession session, String language)
- l This method is for application developers to define the language for translation in their code.
- l String setLanguageMenu(HttpServletRequest request) This method is similar to getLanguageMenu above, but with different behavior.
- l setMappingModeToNone(HttpServletRequest request) Disable i18n4data function of current page.
- l void setPemissionData(HttpSession session, String dataCatalogList) Define a user which user data's catalog he/she has permission to access (editing in edit page).
- l void setPemissionDataAdmin(HttpSession session, boolean isDataAdmin) Set an user as a user data's administrator, so he/she will has all permission to user data's catalog.
- l void setPemissionMessage(HttpSession session, String messageCatalogList) Define a user which interface message's catalog he/she has permission to access (editing in edit page).
- l void setPemissionMessageAdmin(HttpSession session, boolean isMessageAdmin) Set an user as a interface message's administrator, so he/she will has all permission to interface message's catalog.
8 Examples
There one example to demonstrate the feature of i18n4data. It can be download from sourceforge.net or the project web site.
9 License agreement
The i18n4data use the Apache license 2.0 agreement.
10 Contact address
Huang Neng Geng
Address:
- Computer Technology Department
- Wuxi Institute of Technology
- Wuxi, Jiangsu, China, 214073
- Email: huangng@gmail.com, huangng@yahoo.com
﹛